Moxibustion
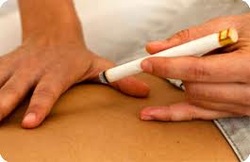 Moxibustion therapy
Moxibustion therapy
Moxibustion is a Traditional Oriental Medicine technique that involves the burning of mugwort, a small, spongy herb, to facilitate healing. Moxibustion has been used throughout Asia for thousands of years; in fact, the actual Asian character for acupuncture, translated literally, means "acupuncture-moxibustion." The purpose of moxibustion, as with most forms of Traditional Oriental Medicine, is to strengthen the blood, stimulate the flow of qi, and maintain general health.
Moxibustion is used on people who have a cold or stagnant condition. The burning of moxa is believed to expel cold and warm the meridians, which leads to smoother flow of blood and qi. In Western medicine, moxibustion has successfully been used to turn breech babies into a normal head-down position prior to childbirth. Moxibustion is used for the treatment of a wide range of disorders, especially neurological and musculoskeletal ones. It is also used regularly for the prevention of illness and the maintenance of health and well being. Often this modality is used for arthritis, digestive issues and gynecological disorders.
Moxibustion is used on people who have a cold or stagnant condition. The burning of moxa is believed to expel cold and warm the meridians, which leads to smoother flow of blood and qi. In Western medicine, moxibustion has successfully been used to turn breech babies into a normal head-down position prior to childbirth. Moxibustion is used for the treatment of a wide range of disorders, especially neurological and musculoskeletal ones. It is also used regularly for the prevention of illness and the maintenance of health and well being. Often this modality is used for arthritis, digestive issues and gynecological disorders.
